Flock Locator
As of August 5th, 2025, Golaem will no longer provide direct support.
All support for Autodesk Golaem will now be handled exclusively through Autodesk support channels and this website will be deactivated soon.
Please bookmark the Autodesk Golaem Support section for any future support needs related to Autodesk Golaem packages.
The Flock Locator defines the volume in which flocks can move thanks to the Flock and Steer behaviors.
a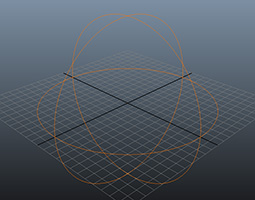
CREATION
A Flock Locator is automatically created when a Flock or a Steer behavior is added to the simulation.
- Golaem Shelf:
 / right click / Flock Locator
/ right click / Flock Locator - Golaem Menu: Environments / Flock Locator
- MEL command: glmFlockLocatorCmd;
Preliminary Notes
Golaem Crowd flock implementation is based on Craig Reynolds' Boids.
Each flock entity is a boid. Each boid has 3 basic rules in addition to optional steering behavior:
- Separation : avoid crowding with neighbors
- Alignment: try to align its velocity with neighbors
- Cohesion: try to stay near neighbors
For each of these rules, a specific neighborhood is considered. The neighborhood is defined by a radius around the current boid, and an angle with current boid direction. All boids outside of radius, or forming an angle with boid velocity wider than angle, are ignored. Additionnaly all boids inside 3*boid radius will be considered in neighborhood so the boid radius, defined when generating from Population Tool, has a strong impact on the final flock homogeneity : greater radius will lead to more separation, cohesion and alignment.
Known limitations
- The flock locator can only be a sphere (i.e. cannot use meshes as flock containers).
- Locator keyframed positions, size and scale will be ignored. Flock Locator radius and position are evaluated at start frame.
- Goalem Crowd Flock does not provide an out of the box solution for controlling yaw/pitch/roll limitations on boids.
CONFIGURATION
Flock Attributes
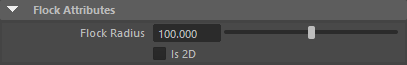
| Flock radius | Controls the enclosing volume of the flock. Boids will tend to stay in this volume but they may wander outside of this radius. |
| is 2D | In 2D mode, flock will drive boids to avoid themselves in a XZ plane only. |
Weights Attributes
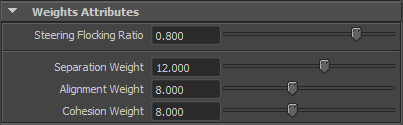
| Steering Flocking Ratio | Depending on the desired result, one can choose to emphasize on steering toward a target (flee/seek/wander), or on flocking effect. A ratio of 0 will negate flocking effect, and just steer toward the current target. A ratio of 1 will only apply flocking effect and won't steer at all. Beware than only applying flocking effect won't move a boid, if it has no other boids in its neighborhood (because no cohesion/separation/alignment can be determined in that case). A ratio of 0.8 is given by default : mostly flocking, while still keeping some steering influence. |
| Separation Weight | Weight of separation in boid final decision. When null, boids will crowd in some points, while great values make them split as much as possible |
| Alignment Weight | Weight of alignment in boid final decision. Try to align boids velocity with their neighbors |
| Cohesion Weight | Weight of cohesion in boid final decision. Try to make boids stay near neighbors |
Boid Neighborhood Perception Attributes
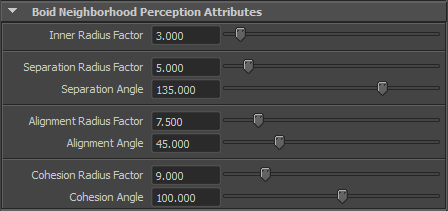
| Inner radius Factor | Controls the radius in which all boids will be considered as neighbors, expressed as an entity radius factor. This neighborhood is used by all goals, in addition to each specific neighborhood definition. |
| Separation Radius Factor | Boid neighborhood radius factor for separation, expressed as an entity radius factor |
| Separation Angle | Boid neighborhood angle for separation |
| Alignment Radius Factor | Boid neighborhood radius factor for alignment, expressed as an entity radius factor |
| Alignment Angle | Boid neighborhood angle for alignment |
| Cohesion Radius Factor | Boid neighborhood radius factor for cohesion, expressed as an entity radius factor |
| Cohesion Angle | Boid neighborhood angle for cohesion |
Obstacles Attributes
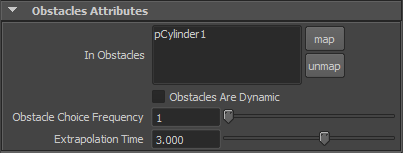
| In Obstacles | Maya meshes mapped to this field to will be avoided by flock |
| Obstacle Choice Frequency | Each boid will avoid nearest obstacle at such frequency. For free flights and random obstacles, a frequency of 1 to 3 should be sufficient. To constrain boids inside a given volume, the frequency must be higher (around 10) to detect properly the volume and to avoid flying through a face while avoiding the last detected one. This parameter will have to be set accordingly to max speed / acceleration and extrapolation time of the boids. |
| Extrapolation Time | Each boid will interpolate its current speed on the given time, to test if it intersects a mesh face. The closest intersection found, if any, will generate a repulsion base on the intersection face normal and current boid speed/direction. |
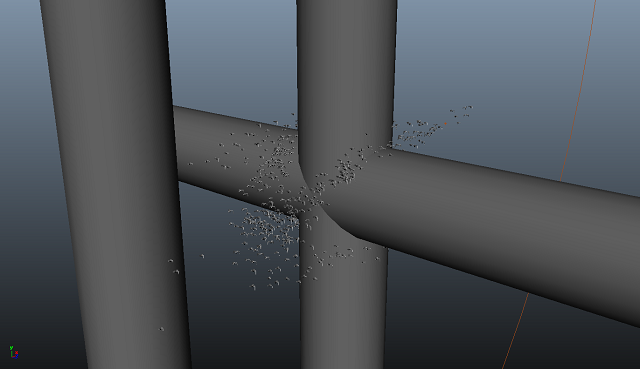
Maya Mesh flock avoidance