Mass-Spring
As of August 5th, 2025, Golaem will no longer provide direct support.
All support for Autodesk Golaem will now be handled exclusively through Autodesk support channels and this website will be deactivated soon.
Please bookmark the Autodesk Golaem Support section for any future support needs related to Autodesk Golaem packages.
A MassSpring Behavior (beMassSpring) adds inertia to one, or several, bone chain(s), according to some spring and damping coefficients.
This behavior generates an acceleration on the end bone, on which IK is applied. It is computed according to this formula (mass is considered to be integrated in the coefficients) :
acceleration = spring * (current behavior position - posture input position) - damping * current behavior 3D speed;
Creation
- Behavior Editor / Behavior Library:

- Golaem Menu: Crowd Behaviors / Behaviors / CrowdBeMassSpring Node
- MEL command: glmCrowdBeMassSpringCmd;
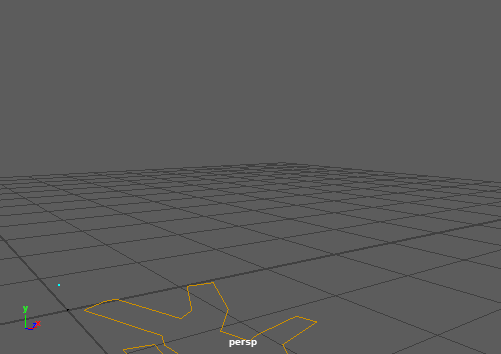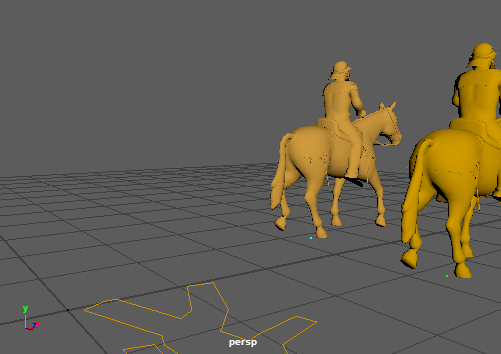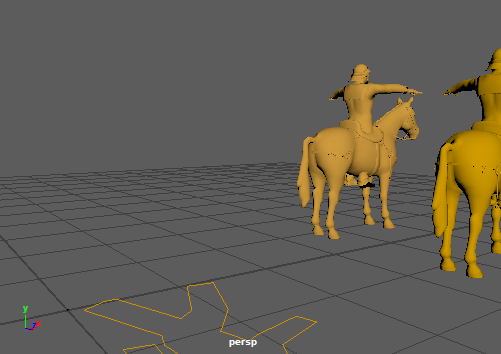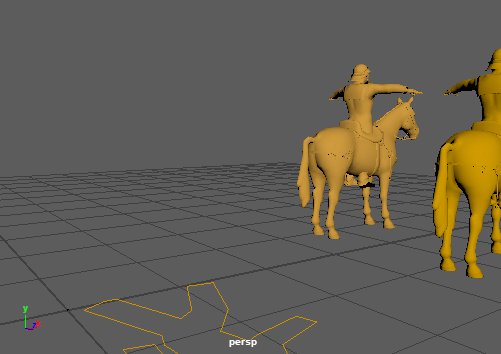
Two horses walking, the one on the foreground also have a MassSpring behavior on the tail
Configuration
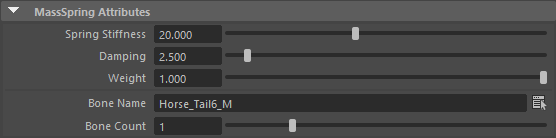
| Spring Stiffness |
The spring stiffness. Higher stiffness leads to more rigid behaviors. |
| Damping | The damping coefficient, which must always be less than the spring stiffness (or resonance will occur). Higher damping avoids oscillations, whereas lower damping allows them. |
| (Weight) | (If several MassSpring Behaviors are active on the same bone chain, this defines the weight to blend them.) This parameter has been deprecated. Due to the mass spring logic, current target correction is reinjected when computing next target. This leads to a fast dropping influence as soon as we move weight below 1.0. The visual influence of the drop down is not a percentage of amplitude as one would expect. The amount of application of the mass spring should be fine tuned with stiffness and damping. |
| Bone Name |
The name of the bone chain ending bone : the "leaf" bone of the chain. |
| Bone Count | The skeleton bone count in the bone chain, impacted by the effect : the last bone of the chain will be the bone name, and it will take (bone count -1) parents in its influence |
Starting / Stopping Duration Attributes
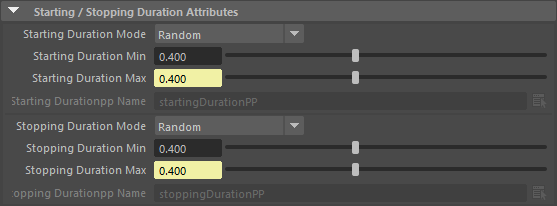
| Starting / Stopping Duration Mode |
This attribute allows a choice of two modes :
The Starting / Stopping Duration value is in seconds. |
| Starting / Stopping Duration Min | See Random option of the Starting / Stopping Duration Mode above Available only when the Starting / Stopping Duration Mode is set to "Random" |
| Starting / Stopping Duration Max | See Random option of the Starting / Stopping Duration Mode above Available only when the Starting / Stopping Duration Mode is set to "Random" |
| Starting / Stopping Durationpp Name | Name of the float per-particle field of the relative particle system, containing the Starting / Stopping Duration Mode value which will be used (for more explanation about how to use ppAttributes, see ppAttributes Handling) Starting / Stopping Duration value is set to 0 if the ppAttribute name is empty or invalid Available only when the Starting / Stopping Duration Mode is set to "Per-Particle Attribute" |